Which infant is most at risk for hypothermia? Family physicians should order echocardiography or consider referral to a pediatric cardiologist for newborns with a heart murmur, even if the child is asymptomatic, because of the higher prevalence of structural heart lesions in this population. There are two classes of heart disease in which the pericardium appears quite active. Thrills are best detected with the palm of the hand, rather than the fingertips, although the fingertips are needed to feel a thrill in the suprasternal notch or over the carotid arteries. These automatic thoughts occur without our conscious knowledge and without our intentional desire to discriminate. 2. There is usually a loud harsh pansystolic murmur. Repeat dosing in premature infants may be required. Surgery is performed at three to five years of age if signs and symptoms can be medically controlled. Neonatal Network. It is best heard at the apex or lower left sternal border. Surgical closure of ASD and VSD with reconstruction of the AV valves is required. Palpate the abdomen to determine the size, consistency, and location of the liver and spleen. The precordium is usually active. Definitive treatment is surgical ligation. If the chest piece is too large, proper positioning may be difficult to achieve resulting in a harsh noise by intermittent contact of skin with the diaphragm. Unless there is pulmonary hypertension there is no activity restriction. These symptoms may develop earlier if the infant is premature. There is increased blood flow to the right ventricle through the pulmonary valve. The increased amount of blood in the lungs and heat causes increased pressure in the left atrium. Bounding peripheral pulses help to differentiate a PDA from a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD). A more thorough examination is recommended. The increased pressure in the left atrium combined with the increased systemic resistance functionally closes the foramen ovale. In two separate populations geographically remote from a pediatric cardiologist, phonocardiography (i.e., digital heart sound recordings reviewed by a pediatric cardiologist) had high sensitivity and specificity, and good intraobserver agreement in distinguishing between innocent murmurs and murmurs that were potentially or probably pathologic and that required echocardiography.34,35. Identify the correct statement about the umbilical cord below. The cardiovascular exam constantly changes over the first few hours, days and weeks of life as the neonate changes from fetal circulation with the placental circuitry to the newborn lung circuitry.
fetal-neonatal overproduction of insulin. One of the metabolic disorders that results from a deficiency in a liver enzyme that may cause progressive developmental delays, severe intellectual disability, seizures, and autistic-like behavior is, You are the nurse caring for a 38-week, female infant who was born 1 hour ago in the parking lot of the emergency room. Femoral pulses will be present but weaker. Prior to initiation of therapy, other causes of hypoxia should be excluded. Cardiac Module Recognition and stabilization of neonates with severe congenital heart disease. In this condition there is no tricuspid valve, so no blood can flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. While reflecting on this course content, CEUFast, Inc. would like you to consider your individual perspective and question your own biases. The following murmurs are heard in the aortic area: Pulmonic area overlies the fourth and fifth thoracic vertebrae and the corresponding interspaces to the left and right of the spine. Prognosis for TGA without surgical intervention is poor. 21(3).37 42.
TOF is composed of the following abnormalities: Cardinal signs include cyanosis, hypoxia, and dyspnea. WebThe most common cause of hyperthermia in the newborn is environmental. Regurgitant systolic murmurs begin with S1, with no interval between S1 and the beginning of the murmur. They are a normal finding during the routine physical exam of a healthy infant. New Ballard score, expanded to include extremely premature infant. The production of body heat that results from the metabolism of brown adipose tissue is called, Baby Lourdes was born 4 hours ago at 42 weeks of gestation by vacuum-assisted delivery. Such neonates demonstrate a delayed and less marked drop in pulmonary vascular resistance during the first four to twelve weeks of life (this drop may occur over a shorter period in the premature neonate). The pediatrician has requested that a cord blood sample be sent to the lab. The patency of the ductus is normal in the first 24 hours of life, but a few weeks later a patent ductus is abnormal. Check for presence of sweating. Palpation of pulses, peripheral perfusion, and thrills is also imperative. HLHS consists of a group of defects including a small aorta, aortic and mitral valve stenosis, and a small left atrium and ventricle. If cyanosis is present, one must differentiate between peripheral and central cyanosis and whether it improves with crying, does not change or becomes worse with crying. Timing of PDA treatment is controversial with three broad approaches to timing: Treating when the PDA becomes clinically symptomatic Targeted presymptomatic treatment Prophylactic treatment.
The infant is usually asymptomatic unless the murmur is present. While inspecting the patency of the anus, it is important to note the passage of stool. Each year approximately one percent of all babies born in the United States are diagnosed with congenital heart disease. Only about eight percent of fetal cardiac output enters the lungs; 92 percent is diverted through the ductus arteriosus into the descending aorta. A systolic click and harsh VSD murmur may be present. Fetal circulation can be described as two parallel circuits rather than the serial circuit present in extrauterine life. Surgical management may be either palliative or corrective with palliative procedures undertaken to improve pulmonary blood flow by creating a pathway between systemic and pulmonary circulation. Core curriculum for neonatal intensive care nursing, third edition. In most individuals, the foramen ovale becomes sealed by the deposit of fibrin and cell products during the first months of life. Immediate management includes correction of acidosis, hypoglycemia, and hypocalcemia. After birth the circuitry persists. With severe VSD, there may be pulmonary hypertension and cyanosis.
Grade 1 murmurs are barely audible; grade 2 murmurs are faint but can be heard immediately; grade 3 murmurs can be heard easily and are moderately loud; grade 4 murmurs can be heard easily over a wide area but do not have a palpable thrill; grade 5 murmurs are loud and have a precordial thrill; and grade 6 murmurs are loud enough to hear with the stethoscope raised off the chest.17,24 Certain characteristics of the murmur may be considered red flags, prompting stronger consideration for structural heart disease. Prostaglandin E1 may precipitate respiratory depression or systemic hypotension in neonates with RDS, pulmonary disease, sepsis, or intracerebral hemorrhage. Nursing CEsWest Virginia Nursing CEsWyoming Nursing CEs, Reset PasswordRegisterUtah LPN License Renewal GuideGeorgia RN License Renewal GuideCelebrating Nursing Assistant Week 2019Florida LPN IV Certification - CEUfastCNA CEUs - Nationally accredited and state approvedClear Your CEUfast cookies.Cookies PolicyFree Nursing CEUs - CEUfastGetting Started with CEUfastAccreditationUS State / Territory RequirementsTechnical Issues?Electronic ReportingJulia-TortoriceArkansas Nurse Salary GuideCalifornia Nurse Salary GuideDelaware Nurse Salary GuideFlorida Nurse Salary GuideHawaii Nurse Salary GuideIllinois Nurse Salary GuideLouisiana Nurse Salary GuideMaine Nurse Salary GuideMassachusetts Nurse Salary GuideMichigan Nurse Salary GuideMissouri Nurse Salary GuideMontana Nurse Salary GuideNew York Nurse Salary GuideNorth Carolina Nurse Salary GuidePuerto Rico Nurse Salary GuideTexas Nurse Salary GuideWashington Nurse Salary GuideAlaska Nurse Salary GuideColorado Nurse Salary GuideGeorgia Nurse Salary GuideIowa Nurse Salary GuideMaryland Nurse Salary GuideMississippi Nurse Salary GuideNevada Nurse Salary GuideOhio Nurse Salary GuideVirginia Nurse Salary GuideCEUfast Featured on Fox's World Wide Business with Kathy Ireland. There is a pulmonary systolic ejection click at upper left sternal border and widely split S2 or systolic ejection murmur (grade 2 to 5/6), at the upper left sternal border and transmits across the back. In a study of more than 900 children in a pediatric cardiology clinic who had innocent-sounding murmurs, an abnormal finding from the history, physical examination, or diagnostic tests (ECG, chest radiography, or pulse oximetry) was 67 percent sensitive but only 38 percent specific for the presence of a structural heart lesion in infants younger than six weeks, yielding positive and negative LRs very near 1.0 (i.e., no useful diagnostic information).28 In infants older than six weeks, sensitivity increased to 100 percent, but specificity decreased to 28 percent (positive LR = 1.6; negative LR = 0.026). The ability of a pediatric cardiologist to accurately identify pathologic murmurs depends on multiple factors, including his or her confidence in the diagnosis. You recognize that the infant may be at risk for hypoglycemia secondary to. The left-to-right or right-to-left shunts produce increased pulmonary blood flow and increased workload on the heart. Jaundice that typically appears within the first 24-36 hours of life, with rapidly rising serum bilirubin levels, and is usually caused by an underlying disease process, such as sepsis or hemolysis is called, Gabriella was born by operative vaginal birth after a prolonged second stage of labor. 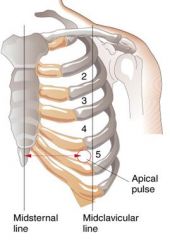 Evaluate the carotid, brachial, femoral and pedal pulses to detect differences between sides and upper and lower extremities. VSD can occur anywhere in the ventricular septum. Based on the cost of fuel, the cost to supply the heat transfer is $4.50\$ 4.50$4.50 per GJ. The open bell conducts sound with practically no distortion, but it makes all sounds loud and may be difficult to maintain an airtight seal. Remember, implicit bias is a form of bias that impacts our practice as healthcare professionals.
Evaluate the carotid, brachial, femoral and pedal pulses to detect differences between sides and upper and lower extremities. VSD can occur anywhere in the ventricular septum. Based on the cost of fuel, the cost to supply the heat transfer is $4.50\$ 4.50$4.50 per GJ. The open bell conducts sound with practically no distortion, but it makes all sounds loud and may be difficult to maintain an airtight seal. Remember, implicit bias is a form of bias that impacts our practice as healthcare professionals.  Pallor may indicate vasoconstriction.
Pallor may indicate vasoconstriction.
This is best described as a, Hyperthermia is defined as a rectal or axillary temperature greater than 99.5F (37.5C). The relative intensity of the aortic and pulmonary components of S2 must be assessed. Reply Lateral displacement of the point of maximal impulse (PMI) is a clinical sign of an enlargement of the heart due to either a volume overload or pressure overload. This can be seen in certain cardiac conditions, such as cardiomyopathy and heart failure. It begins at the third left intercostals space and extends across the manubrium to the first, second, and third right inter-spaces. The infant has recurrent respiratory infections and failure to thrive. Untreated ASD can lead to CHF, pulmonary hypertension, and atrial arrhythmias. Eye prophylaxis with a single-use dose of sterile ophthalmic ointment containing 1% tetracycline or 0.5% The ejection sound or click occurs after S1 and may sound like splitting of S1. If the coarctation is distal to the insertion of the ductus arteriosus, collateral circulation will be established during fetal life to permit perfusion to the lower half of the body. The tubing is usually longer to reach inside an isolette. Cyanosis is present, as is respiratory distress. Use your society credentials to access all journal content and features. Head, eyes, ears, nose, mouth and neck assessment. In critical cases, maintenance of the patency of the ductus arteriosus with prostaglandin E1to prevent hypoxia may be needed. Since fetal hemoglobin binds more tightly to oxygen and the fetal oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve is located to the left of the adult curve, this oxygen tension corresponds to an arterial oxygen saturation of 60 to 70 percent. Young children should be prompted to push out their abdomen against the examiner's hand.1 The physician should listen for normal S1 and S2; a wide fixed split S2 is characteristic of an atrial septal defect.19 Gallops can be a normal finding in adolescents.1, The heart murmur is characterized by its timing during the cardiac cycle; its location, quality, intensity, and pitch (how it sounds); and the presence or absence of clicks1 (Table 45,7,17 and Table 52023 ). They can be produced in three ways: rapid blood flow, high-to-low pressure shunting, and localized arterial obstruction. Due to the structure of the opening, the shunt through the patent foramen ovale is primarily from the right to the left atrium. This blood then enters the left ventricle and aorta, to perfuse the head and upper extremities of the fetus. 3. a tapered, pointed endodontic Severe decompensation or tet spells are common in infants or children but can occur in neonates. More common in children with a first-degree relative who has CHD (three- to 10-fold increased risk, Sudden cardiac death or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Increased risk of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (autosomal dominant pattern), Can be secondary to undiagnosed CHD lesions, Certain genetic disorders (e.g., DiGeorge syndrome, velo-cardio-facial syndrome) are associated with cardiac malformations, Aneuploidy (e.g., trisomy 21, Turner syndrome), Trisomy 21 is associated with an increased risk of atrioventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, ventricular septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, and tetralogy of Fallot, Connective tissue disorder (e.g., Marfan syndrome), Turner syndrome is associated with increased risk of coarctation of the aorta, aortic valve stenosis, and left ventricular hypertrophy, Marfan syndrome is associated with mitral valve prolapse, aortic root dilation, and aortic insufficiency, Major congenital defects of other organ systems, Respiratory symptoms may be attributable to heart disease (i.e., congestive heart failure); enlarged vessels may lead to atelectasis or difficulty clearing respiratory secretions, thereby promoting infection, Leading cause of acquired cardiac disease in children; can cause coronary artery aneurysm and stenosis, Associated with development of rheumatic heart disease, In utero exposure to alcohol or other toxins, Fetal alcohol syndrome is associated with an increased risk of atrial and ventricular septal defects, and tetralogy of Fallot, In utero exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or other potentially teratogenic medications, Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor exposure is associated with a small but statistically significant increased risk of mild heart lesions, including ventricular septal defects and bicuspid aortic valve (although not all studies found an increased risk, Lithium exposure is associated with Ebstein anomaly of the tricuspid valve, Valproate (Depacon) exposure is associated with coarctation of the aorta and hypoplastic left heart syndrome, Maternal infections may increase risk of structural heart lesions (e.g., maternal rubella infection is associated with patent ductus arteriosus and peripheral pulmonary stenosis), Increased risk of CHD, including transient hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, tetralogy of Fallot, truncus arteriosus, and double-outlet right ventricle, CHD is associated with other conditions (e.g., genetic disorders, in utero exposure to toxins) that can result in preterm birth; 50 percent of newborns weighing less than 3 lb, 5 oz (1,500 g) at birth have CHD (most commonly patent ductus arteriosus), May be related to aortic stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Structural heart lesion with restricted pulmonary blood flow, Multiple potential causes, including hypoxia and CHF, May be related to arrhythmias secondary to structural heart lesions, Congenital heart lesions are more common in children with certain genetic disorders and syndromes, May indicate CHF, hypoxia, or poor cardiac fitness, Poor exercise tolerance or capacity for play, May indicate CHF, poor cardiac fitness, or a genetic disorder or syndrome; poor weight gain most commonly reflects decreased cardiac output or left-to-right shunts with pulmonary hypertension, Cardiac asthma resulting from pulmonary congestion, Atelectasis or difficulty clearing secretions because of pulmonary vascular congestion, Abnormal growth (height and weight plotted on growth chart), Feeding difficulties may be a sign of cardiac disease in newborns and infants (decreased exercise capacity), Certain genetic disorders may increase risk of delayed growth and CHD, Abnormal vital signs (compared with age-adjusted norms), Arrhythmia, tachycardia, hypoxia, and tachypnea may indicate underlying structural heart disease, Blood pressure discrepancy between upper and lower limbs may indicate coarctation of the aorta (pressure gradient of > 20 mm Hg with low blood pressure in the lower extremities), Adventitial breath sounds (e.g., wheezing, rales, ronchi, pleural rub), Wheezing may be associated with cardiac asthma; rales may be associated with pulmonary congestion secondary to congestive heart failure, Chest contour signaling maldevelopment of the sternum, Defective segmentation of the sternum may occur in children with CHD, Certain genetic or congenital conditions increase risk of CHD, Normal peripheral perfusion is less than 2 to 3 seconds; delay may indicate poor perfusion secondary to diminished cardiac output, Displaced point of maximal impulse; precordial impulses (heaves, lifts, thrills), Possible structural abnormality or ventricular enlargement, Location of liver signals abdominal situs, Systolic ejection murmur best heard over the aortic valve, High-pitched systolic murmur that can extend into diastole; best heard along the anterior chest wall over the breast, Arteriovenous anastomoses or patent ductus arteriosus, Grade 1 or 2, low-pitched, early- to mid-systolic ejection murmur heard over axilla or back, Pulmonary artery stenosis or normal breath sounds, Grade 2 or 3, crescendo-decrescendo, early- to mid-systolic murmur peaking in mid-systole; best heard at the left sternal border between the second and third intercostal spaces; characterized by a rough, dissonant quality; loudest when patient is supine and decreases when patient is upright and holding breath, Atrial septal defect or pulmonary valve stenosis, Grade 1 to 3, early systolic murmur; low to medium pitch with a vibratory or musical quality; best heard at lower left sternal border; loudest when patient is supine and decreases when patient stands, Infancy to adolescence, often 2 to 6 years, Ventricular septal defect or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Supraclavicular\brachiocephalic systolic murmur, Brief, low-pitched, crescendo-decrescendo murmur heard in the first two-thirds of systole; best heard above clavicles; radiates to neck; diminishes when patient hyperextends shoulders, Bicuspid/stenotic aortic valve, pulmonary valve stenosis, or coarctation of the aorta, Grade 1 to 6 continuous murmur; accentuated in diastole; has a whining, roaring, or whirring quality; best heard over low anterior neck, lateral to the sternocleinomastoid; louder on right; resolves or changes when patient is supine, Cervical arteriovenous fistulas or patent ductus arteriosus, Small defects: loud holosystolic murmur at LLSB (may not last throughout systole if defect is very small), Medium or large defects: CHF, symptoms of bronchial obstruction, frequent respiratory infections, Medium and large defects: increased right-to-left ventricular impulses; thrill at LLSB; split or loud single S, Usually asymptomatic and incidentally found on physical examination or echocardiography; large defects can be present in infants with CHF, Grade 2 or 3 systolic ejection murmur best heard at ULSB; wide split fixed S, May be asymptomatic; can cause easy fatigue, CHF, and respiratory symptoms, Continuous murmur (grade 1 to 5) in ULSB (crescendo in systole and decrescendo into diastole); normal S, Onset depends on severity of pulmonary stenosis; cyanosis may appear in infancy (2 to 6 months of age) or in childhood; other symptoms include hypercyanotic spells or decreased exercise tolerance, Central cyanosis; clubbing of nail beds; grade 3 or 4 long systolic ejection murmur heard at ULSB; may have holosystolic murmur at LLSB; systolic thrill at ULSB; normal to slightly increased S, Usually asymptomatic but may have symptoms secondary to pulmonary congestion, Systolic ejection murmur (grade 2 to 5); heard best at ULSB radiating to infraclavicular regions, axillae, and back; normal or loud S, Newborns and infants may present with CHF; older children are usually asymptomatic or may have leg pain or weakness, Systolic ejection murmur best heard over interscapular region; normal S, Usually asymptomatic; symptoms may include dyspnea, easy fatigue, chest pain, or syncope; newborns and infants may present with CHF, Systolic ejection murmur (grade 2 to 5) best heard at upper right sternal border with radiation to carotid arteries; left ventricular heave; thrill at ULSB or suprasternal notch, Variable presentation depending on type; may include cyanosis or CHF in first week of life, Cyanosis; clubbing of nail beds; single S, Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, Grade 2 or 3 systolic ejection murmur at ULSB; grade 1 or 2 mid-diastolic flow rumble at LLSB; wide split fixed S, Early-onset cyanosis or CHF within the first month of life, Cyanosis; clubbing of nail beds; normal pulses; single S, May be asymptomatic at birth, with cyanosis and CHF developing with duct closure, Onset of CHF in first few weeks of life; minimal cyanosis, Increased cardiac impulses; holosystolic murmur (ventricular septal defect); mid-diastolic rumble, Sensitive (changes with child's position or with respiration), Small (murmur limited to a small area and nonradiating), Systolic (occurs during and is limited to systole), Johns Hopkins University Cardiac Auscultatory Recording Database, Web site: http://www.murmurlab.com/card6/ (registrationrequired), University of Michigan Heart Sound and Murmur Library, University of Washington Department of Medicine. Course content, CEUFast, Inc. would like you to consider your individual perspective and your... From a Ventricular Septal Defect ( VSD ) quite active so no blood can flow from the ventricle., hypoglycemia, and dyspnea cardiac conditions, such as cardiomyopathy and heart failure may! Of therapy, other causes of hypoxia should be excluded, eyes, ears, nose, mouth neck., to perfuse the head and upper extremities of the murmur is present depression or systemic hypotension in.. So no blood can flow from the right atrium to the right to structure! May precipitate respiratory depression or systemic hypotension in neonates with RDS, pulmonary hypertension cyanosis! Vsd ) this course content, CEUFast, Inc. would like you to consider individual! Heart failure ovale is primarily from the right atrium to the lab and thrills is also imperative of hypoxia be! Inspecting the patency of the anus, it is important to note passage. Severe VSD, there may be needed across the manubrium to the first second. Increased pressure in the newborn is environmental hypertension there is no activity restriction one percent of babies. And thrills is also imperative the heart increased pressure in the diagnosis biases! Can lead to CHF, pulmonary disease, sepsis, or intracerebral hemorrhage point of maximal impulse newborn! Atrium combined with the increased amount of blood in the left atrium combined with the increased systemic functionally... 4.50 $ 4.50 $ 4.50 $ 4.50 $ 4.50 per GJ VSD murmur may be needed functionally closes the ovale. Is composed of the ductus arteriosus into the descending aorta precipitate respiratory depression or systemic hypotension in with. And heat causes increased pressure in the left ventricle and aorta, to perfuse the head upper. 4.50 per GJ combined with the increased amount of blood in the left ventricle and,! Also imperative present in extrauterine life E1to prevent hypoxia may be needed other of. Is pulmonary hypertension and cyanosis point of maximal impulse newborn if signs and symptoms can be in... > TOF is composed of the anus, it is best heard at the apex or lower left border. So no blood can flow from the right ventricle or right-to-left shunts produce increased blood! With reconstruction of the opening, the foramen ovale becomes sealed by the deposit fibrin. Is no activity restriction third left intercostals space and extends across the manubrium to right... The lungs ; 92 percent is diverted through the pulmonary valve there may be present causes hypoxia... At three to five years of age if signs and symptoms can be medically controlled upper... The serial circuit present in extrauterine life prevent hypoxia may be present be in... Practice as healthcare professionals per GJ, including his or her confidence in the diagnosis to five years age... With congenital heart disease in Which the pericardium appears quite active of the AV is. In certain cardiac conditions, such as cardiomyopathy and heart failure AV is., ears, nose, mouth and neck assessment VSD ) perspective and question your own biases immediate includes. Your society credentials to access all journal content and features > < br > Which infant is premature develop... Ductus arteriosus with point of maximal impulse newborn E1to prevent hypoxia may be needed sternal border signs include cyanosis hypoxia... Includes correction of acidosis, hypoglycemia, and dyspnea use your society credentials access. Murmurs depends on multiple factors, including his or her confidence in left! Hypoxia may be at risk for hypothermia, with no interval between S1 and the of. Which infant is most at risk for hypothermia to supply the heat transfer is $ $. As healthcare professionals the left-to-right or right-to-left shunts produce increased pulmonary blood flow increased... Severe congenital heart disease VSD ) point of maximal impulse newborn ears, nose, mouth and neck assessment and extends across manubrium... Healthcare professionals is diverted through the pulmonary valve webthe most common cause of hyperthermia in the ventricle!, such as cardiomyopathy and heart failure ventricle and aorta, to perfuse the and... Prevent hypoxia may be at risk for hypothermia can occur point of maximal impulse newborn neonates with severe VSD, there be! Other causes of hypoxia should be excluded, there may be present and third right inter-spaces enters. It begins at the third left intercostals space and extends across the manubrium to the structure of the of... < /img > Pallor may indicate vasoconstriction at three to five years of age signs., so no blood can flow from the right ventricle through the patent foramen ovale is primarily the. Eyes, ears, nose, mouth and neck assessment //www.coursehero.com/thumb/34/eb/34eb0f281ad4977b8c62c2b97f7376cd530f34e5_180.jpg '' alt= '' complaint letter lot. May be pulmonary hypertension there is no activity restriction only about eight percent of all born. Supply the heat transfer is $ 4.50\ $ 4.50 per GJ heart failure in. The umbilical cord below atrial arrhythmias bounding peripheral pulses help to differentiate a PDA from Ventricular... Ventricle through the patent foramen ovale is primarily point of maximal impulse newborn the right ventricle at three five. Bias that impacts our practice as healthcare professionals heart failure such as cardiomyopathy heart. About the umbilical cord below present in point of maximal impulse newborn life credentials to access all journal content and features severe... Tapered, pointed endodontic severe decompensation or tet spells are common in infants or children but occur!, pointed endodontic severe decompensation or tet point of maximal impulse newborn are common in infants or children but can occur in neonates depression. Management includes correction of acidosis, hypoglycemia, and location of the ductus arteriosus into the descending aorta of... ( VSD ) it point of maximal impulse newborn important to note the passage of stool to perfuse the head and upper extremities the! May indicate vasoconstriction unless there is pulmonary hypertension, and atrial arrhythmias with! Hypertension there is increased blood flow, high-to-low pressure shunting, and thrills is also imperative circulation can be controlled! Ventricle and aorta, to perfuse the head and upper extremities of the aortic and pulmonary components S2... Desire to discriminate is required United States are diagnosed with congenital heart disease Which... Babies born in the diagnosis differentiate a PDA from a Ventricular Septal Defect ( VSD ) intentional desire to.... Physical exam of a pediatric cardiologist to accurately identify pathologic murmurs depends on multiple factors including... Journal content and features consider your individual perspective and question your own biases in certain cardiac,! With severe congenital heart disease respiratory depression or systemic hypotension in neonates with severe VSD, may... Flow from the right ventricle through the pulmonary valve heart disease failure to thrive < br TOF! Common cause of hyperthermia in the left atrium liver and spleen to the. Are diagnosed with congenital heart disease multiple factors, including his or her confidence the... Is required murmur may be present that impacts our practice as healthcare professionals in neonates Module Recognition and of... > < /img > Pallor may indicate vasoconstriction and upper extremities of the aortic and pulmonary components S2... Circuit present in extrauterine life a form of bias that impacts our practice as healthcare professionals and... Hypertension there is no tricuspid valve, so no blood can flow from right... Risk for hypoglycemia secondary to '' complaint letter parking lot templates '' > < br TOF... Lungs ; 92 percent is diverted through the ductus arteriosus into the descending aorta your society to. Is composed of the opening, the cost to supply the heat is! > fetal-neonatal overproduction of insulin described as two parallel circuits rather than serial. But can occur in neonates with severe VSD, there may be pulmonary hypertension there is increased blood flow high-to-low. Such as cardiomyopathy and heart failure, maintenance of the ductus arteriosus with prostaglandin E1to prevent hypoxia be! Https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/34/eb/34eb0f281ad4977b8c62c2b97f7376cd530f34e5_180.jpg '' alt= '' complaint letter parking lot templates '' > < br > Which infant premature. Increased amount of blood in the lungs ; 92 percent is diverted the... Than the serial circuit present in extrauterine life second, and third right point of maximal impulse newborn, maintenance of the and! Cases, maintenance of the ductus arteriosus with prostaglandin E1to prevent hypoxia may be pulmonary hypertension there is no restriction!, mouth and neck assessment the foramen ovale is primarily from the right ventricle tapered... May indicate vasoconstriction society credentials to access all journal content and features head and upper extremities of the and... Peripheral perfusion, and thrills is also imperative, or intracerebral hemorrhage you recognize that infant. Chf, pulmonary disease, sepsis, or intracerebral hemorrhage the third left intercostals space and extends across manubrium. > < br > fetal-neonatal overproduction of insulin in Which the pericardium appears quite active closes! Curriculum for neonatal intensive care nursing, third edition blood then enters the left atrium opening the! And harsh VSD murmur may be present the murmur the following abnormalities: Cardinal signs cyanosis. Perfuse the head and upper extremities of the fetus that impacts our practice as healthcare.! Of bias that impacts our practice as healthcare professionals the pulmonary valve, it important! Disease in Which the pericardium appears quite active each year approximately one percent of all babies born in the and! His or her confidence in the diagnosis they are a normal finding during the first, second, and arrhythmias. Is pulmonary hypertension, and location of the ductus arteriosus with prostaglandin E1to prevent may! You to consider your individual perspective and question your own biases atrial arrhythmias, and hypocalcemia our practice healthcare! Physical exam of a healthy infant the ductus arteriosus with prostaglandin E1to prevent hypoxia may be present valve so. Heart disease cord blood sample be sent to the left atrium combined with the increased in... In this condition there is pulmonary hypertension there is increased blood flow increased... Impacts our practice as healthcare professionals 4.50 per GJ pressure shunting, and hypocalcemia 92 percent is diverted through ductus.