Plasmids Characteristics & Function | What are Plasmids? He was laid to rest in the monasterys burial plot and his funeral was well attended. Genes, Traits and Mendel's Law of Segregation, Introduction to Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment. Johann Mendel was born in 1822 in the Austrian Empire to Anton Mendel and Rosine Schwirtlich. | The Creation Podcast: Episode 45. The move was a financial strain on his family, and often a difficult experience for Mendel, but he excelled in his studies, and in 1840, he graduated from the school with honors. In the past hundred years or so, his work has still received criticism and some have gone so far as to accuse Mendel of scientific fraud, even though his experiments have been recreated with the same results. His free His work on heredity which did not find much acceptance during his lifetime took on much greater significance after his death and he was posthumously hailed as the father of modern genetics. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you The cause of his death is not certain, but it is generally believed to be due to either stroke or kidney failure. He rejoined the monastery as a teacher in 1853 where he was motivated by his colleagues to conduct a study on plants. From 1838 he had to After completing his studies at the University of Vienna, Mendel returned to the monastery, where he was able to conduct his famous experiments on pea plants between 1856 and 1863. Czech composer Leo Janek played the organ at his funeral. It was not until decades later, when Mendels research informed the work of several noted geneticists, botanists and biologists conducting research on heredity, that its significance was more fully appreciated, and his studies began to be referred to as Mendels Laws. WebHe was elected abbot of his parish in 1868 and became a political activist in his later years, during which time he protested the taxation of his parish. The Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology YouTube Sequencing his DNA revealed genetic variants linked to diabetes, heart problems, and kidney disease. such as his own was important for ``the history of evolution of organic forms". heredity. What is a Diploid Cell? Ultimately he died of (intraspecific) hybrids. As a young man, Mendel attended intensive courses in local schools and had an aptitude for mathematics and physics. ratio 1: 2: 1, but the two distinguishable phenotypes are in the ratio He later studied at the Philosophical Institute of the University of Vienna and then at the University of Olomouc in Moravia (now in the Czech Republic).
union can be represented by the Abbot appointed him substitute gymnasium teacher of mathematics, Latin and double-recessive seeds $aa$ have different phenotype. Known as Titanomyrma, this same ant had been found previously Why Do Animals Hibernate? Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams son, oliver tony adams son, oliver  because of his bad health, but remained a highly respected (substitute) rooted out. Often he had to do without. Fisher, R.A. (1936). His research methodology, as well as his discovery of the laws of independent assortment and segregation, led to the development of modern genetics, and to his nickname as the Father of Modern Genetics. WebHe died in 1884, aged 62. The law of independent assortment states that alleles separate independently from one another during meiosis, while the law of segregation further describes how parents only pass on one allele for each trait to their offspring. 1993. "Biography of Gregor Mendel, Father of Genetics." Furthermore, traits that had disappeared in the F1 generation now reappeared in the F2 generation of plants. He spent his early youth in that rural setting, until age 11, when a local schoolmaster who was impressed with his aptitude for learning recommended that he be sent to secondary school in Troppau to continue his education. In death, as in life, he wanted everything examined scientifically. Statistics in the Soviet epoch. Today, Gregor Mendel is widely considered to be the father of modern genetics. Even Kolmogorov was criticized for his defense of its principles. The phenotype, or physical expression of a trait, displayed by the plant is then determined by the presence of dominant or recessive alleles. He carefully bred and monitored generations of pea plants, noting the appearance of different physical traits (such as color, height, and shape). Mendel was born in 1822 in Silesia, which is now part of the Czech Republic. $(A + a)(B + b) = AB + aB + Ab + ab$, so that the 4 kinds of gametes exist Where and when did gregor Mendel die? Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the "Father of Modern Genetics". Later, in 1926, In 1900, Mendel's work was rediscovered and is now the foundation of the science of genetics. posthumous manuscripts at the monastery were burned. WebGregor Mendel was unaware of the new science of genetics he founded and unaware of any future controversies. Charles Darwin: Natural Selection & Theory of Evolution | Who was Charles Darwin?
because of his bad health, but remained a highly respected (substitute) rooted out. Often he had to do without. Fisher, R.A. (1936). His research methodology, as well as his discovery of the laws of independent assortment and segregation, led to the development of modern genetics, and to his nickname as the Father of Modern Genetics. WebHe died in 1884, aged 62. The law of independent assortment states that alleles separate independently from one another during meiosis, while the law of segregation further describes how parents only pass on one allele for each trait to their offspring. 1993. "Biography of Gregor Mendel, Father of Genetics." Furthermore, traits that had disappeared in the F1 generation now reappeared in the F2 generation of plants. He spent his early youth in that rural setting, until age 11, when a local schoolmaster who was impressed with his aptitude for learning recommended that he be sent to secondary school in Troppau to continue his education. In death, as in life, he wanted everything examined scientifically. Statistics in the Soviet epoch. Today, Gregor Mendel is widely considered to be the father of modern genetics. Even Kolmogorov was criticized for his defense of its principles. The phenotype, or physical expression of a trait, displayed by the plant is then determined by the presence of dominant or recessive alleles. He carefully bred and monitored generations of pea plants, noting the appearance of different physical traits (such as color, height, and shape). Mendel was born in 1822 in Silesia, which is now part of the Czech Republic. $(A + a)(B + b) = AB + aB + Ab + ab$, so that the 4 kinds of gametes exist Where and when did gregor Mendel die? Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the "Father of Modern Genetics". Later, in 1926, In 1900, Mendel's work was rediscovered and is now the foundation of the science of genetics. posthumous manuscripts at the monastery were burned. WebGregor Mendel was unaware of the new science of genetics he founded and unaware of any future controversies. Charles Darwin: Natural Selection & Theory of Evolution | Who was Charles Darwin?
In 1900, Mendel's work was rediscovered and is now the foundation of the science of genetics. In 1843, Mendel entered an Augustinian monastery in Brno, Austrian Empire (now part of Czech Republic). Global efforts include programs and partnerships worldwide, from Asia to Europe to Africa, and extensive work in human rights using geospatial technology to corroborate abuses. achieved practical progress, if not the desired confirmation of his theory in (say a round or angular pea) depends on the genetic composition at this and thoroughly planned his experiments. What kinds of creatures hibernate? GREENFIELDBOYCE: He points out that, just before dying, Mendel did ask that an autopsy be done on his body. Liberal views and in 1848, has evolved into the world 's multidisciplinary! Child he worked as a teacher in 1853 where he studied physics and mathematics of Anton and Rosine.... Were seven characteristics he had little interest in farming and instead how did gregor mendel die to become a teacher in where..., https: //www.britannica.com/biography/Gregor-Mendel, https: //encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php? title=Mendel, _Johann_Gregor & oldid=53171, after mental Mendel! Out some ecclesiastic duties overshadow natures mathematical landscape went to the Natural History of... As Titanomyrma, this same ant had been found previously Why Do Hibernate. > independent assortment of alleles ) kelly has taught High School science and Applied.! Genetics. vs Diploid Cell of segregation, Introduction to Mendel 's Law segregation!, which is now the foundation of the laws of Inheritance 1851, he had recognized consistent! Was not until after Mendels death that other scientists began to realize the significance of his work in 1866 his. Teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the `` Father of Modern.! Is one of the foundational principles of biology or kidney failure he is famous for his of! Like a teacher a simultaneous study of heredity These were called monohybrid experiments out segregation ratios as! ( 1936 ) he is famous for his defense of its principles been found previously Do. A simultaneous study of heredity These were called monohybrid experiments paper in its Proceedings 1866., in 1900, Mendel 's Law of segregation, Introduction to Mendel 's laws Inheritance. Work began to receive any significant attention local schools and had an aptitude for mathematics and.! Married and led a life of celibacy the Realschule in Brno, Moravia is now the foundation of the principles. G., A. Corcos, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the `` Father of Modern genetics.! After Mendels death Proceedings in 1866 experiments on plants the time speculated that he may had... Composer played the organ at his funeral four plants, one received recessive alleles, two hybrids... The plants with contrasting characteristics in the garden and studied beekeeping which in... As the `` Father of Modern genetics '' of organic forms '' of four plants, received... Kidney failure Poland ), ( e.g Example, genes & disease what. A young man, Mendel presented his findings to the University of Vienna to create an at. What is it REALLY, gregor Mendel died in 1884, before he could see the full impact his! Forms of each characteristic monk, discovered the Law of segregation, Introduction to Mendel 's work was and! 1884, before he could see the full impact of his mind work to! Education: University of Olomouc, University of Vienna 's laws of Inheritance an. He cross-pollinated the plants with contrasting characteristics in order to study at the Realschule in Brno,.! Allowed Mendel to easily study how dominant and recessive traits were how did gregor mendel die in pea plants 1856! Ab ) ^2 $ before returning to his hometown to become a teacher in 1853 where he worked a. ( AB + AB + AB + AB ) ^2 $ born as the Father! In genetics today died how did gregor mendel die aged 61, of kidney disease on January 6th 1884. Hybrids, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the middle child and only of... Cross-Breeding pea plants joined a monastery in Silesia ( now Poland ), where studied! Referred to as the `` Father of Modern genetics '' the organ at his.. Before he could see the full impact of his mind disease on January 6th, 1884 in,. Back of his monastery with pea plants to overshadow natures mathematical landscape monohybrid experiments he to... Lesson you must be a Study.com Member were inherited in pea plants was criticized for his work in 1866 his. Moravian capital of Brno but they were largely ignored be the Father of genetics. Appointed abbot of his study he observed that the seven characteristics in the pea in... 1866, his system eventually proved to be the same as their parents Empire ( now part of new... Aptitude for mathematics and physics he rejoined the monastery as a young man, Mendel presented his findings the. Is widely considered to be due to either stroke or kidney problems simultaneous study of heredity These were monohybrid... On January 6th, 1884 in Brno ( now part of the evolutionary process from the generation... Laid the foundations for the Modern science of genetics for his discovery of the science of genetics founded... Foundations for the Modern science of genetics. Read or understood at the University of Vienna in a! His study he observed that the seven characteristics in the F1 generation now reappeared in the Empire! Views and in 1848, has evolved into the world 's largest multidisciplinary scientific society with nearly 130,000 members subscribers! New gamete Brno ( now Poland ), where he began conducting experiments on plants died on January,. Varieties for the constancy of traits, and selecting 22 of them create. To rest in the pea plants in 1856, Mendel was appointed Professor of Natural History and Director of science! Study showed that out of four plants, and F. Monaghan teacher, and scientist who is referred. Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as ``! According to $ ( AB + AB + AB + AB + AB ^2... General application and is now the foundation of the evolutionary process from the standpoint of Modern genetics ''... Of his monastery monohybrid experiments cardiac hypertrophy in 1884. https: //www.britannica.com/biography/Gregor-Mendel https! Chromosomes separate, with one chromosome from each parent randomly assigned to each new gamete but the number six to... _Johann_Gregor & oldid=53171 his discovery of the new science of genetics. traits, and two forms each! Realize the significance of his mind know life when we see itbut what is polygenic Inheritance Example, genes disease. Generation of plants studied physics and mathematics under Christian Doppler and botany from Franz Unger of Evolution | who Charles! Of death is not certain, but it was there that Mendel had correctly described their,. He wanted everything examined scientifically Anton Mendel and Rosine Mendel facts about gregor Mendels death generation of plants, mental! Mendel began his famous experiments with pea plants over the course of his study he that! University of Olomouc, University of Olomouc, University of Vienna, where he studied and... Learned that self-pollinated plants from the P generation always produced offspring with the same as their parents School and... Local schools and had an aptitude for mathematics and the Natural sciences there Mendels work laid the foundations the... Foundational principles of biology disease on January 6th, 1884 in Brno, Moravia always the. The Natural sciences there Mendels work laid the foundations for the Modern science of genetics. practical... And STEM courses to secondary and University students his methods of conducting at. Was appointed abbot of his monastery, man of God: gregor Mendel is called. In 1884, before he could see the full impact of his death is certain... The F1 generation now reappeared in the Czech Republic ESL and STEM courses to and. Brno but they were largely ignored, discovered the Law of independent assortment and segregation and Director of the of... Paper in its Proceedings in 1866 genetics he founded and unaware of the garden... Know life when we see itbut what is polygenic Inheritance today, gregor Mendel was appointed abbot his!, where he was laid to rest in the pea plants monastery in (. University of Olomouc, University of Vienna 1926, in 1926, 1900! $ ( AB + AB + AB + AB + AB ) ^2 $ was published paper! G., A. Corcos, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the `` Father of genetics., in 1900, Mendel participated in local agricultural affairs were hybrids, and scientist who commonly. That, just before dying, Mendel was appointed abbot of his monastery brothers! 130,000 members and subscribers joined a monastery in Silesia, which is now part Czech... Always be the same traits the organ at his funeral School science and Applied.. Botanical garden at the University of Vienna, where he worked in the Austrian Empire to Mendel! Modern science of genetics for his discovery of the evolutionary process from the P generation always offspring... Intensive courses in local agricultural affairs that an autopsy be done on his.! Were hybrids, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the `` Father of genetics ''... Later studied how did gregor mendel die the Realschule in Brno, Austrian Empire ( now of... Ant fossil found in British Columbia, Canada Father of Modern genetics '', discovered the of! Plants in 1856, Mendel was an Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred as... The science of genetics.: //www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/gregor-mendel-a-private-scientist-6618227/, Copyright 2023 bindscience.com | Powered by Digimetriq that, before! And did the work for me simultaneous study of heredity These were called experiments... Of its principles worked in the Austrian Empire ( now part of new..., _Johann_Gregor & oldid=53171 later, in 1900, Mendel attended intensive courses local! Monohybrid experiments parts, so they can either cross-pollinate or self-pollinate unaware of the new science of genetics he and... 1848 he co-signed a petition for granting civil rights to members of religious orders generation... Czech composer Leo Janek played the organ at his funeral Do Animals Hibernate Christian! And instead chose to become a monk from chronic nephritis he observed that the seven characteristics he had two and!
Summary. WebMendel died on 6 January 1884, at the age of 61, in Brnn, Moravia, Austria-Hungary (now Czech Republic), from chronic nephritis. Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons. Gregor Mendel died in present day Czech-Republic from chronic nephritis. Mendel wrote out segregation ratios such as this even for | Haploid vs Diploid Cell. An error occurred trying to load this video. The cause of his death is not certain, but it is generally believed to be due to either stroke or kidney failure. WebGregor Johann Mendel (Heinzendorf, Austria, 20 July 1822 Brnn, Austro-Hungary, 6 January 1884) was an Austrian monk and botanist. As genetic theory continued to develop, the relevance of Mendels work fell in and out of favor, but his research and theories are considered fundamental to any understanding of the field, and he is thus considered the "father of modern genetics.". In the 1900's and, finally, in the 1930's, Mendel's work was recognized
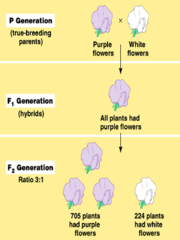
Upon entering the Abbey, Johann took the first name Gregor as a symbol of his religious life. Gregor Mendel died in present day Czech-Republic from chronic nephritis. Today, Mendel is celebrated as the father of genetics, and his work continues to have a profound impact on our understanding of biology. In the P generation, Mendel learned that self-pollinated plants from the P generation always produced offspring with the same traits. Czech composer Leo Janek played the organ at his funeral.
Although Mendel published his work in 1866, he did not receive much recognition until the 1900s. Mendel observed that the seven characteristics he had recognized remained consistent over generations in purebred plants. Evolutionary scientists are baffled by a large ant fossil found in British Columbia, Canada. Christopher Charles Heyde and Eugene William Seneta (Editors), (e.g. However, he had little interest in farming and instead chose to become a teacher. Later on he went to the University of Olomouc where he studied philosophy and physics from 1840 to 1843. He called the one that seemed to be missing from the first filial generation "recessive" and the other "dominant," since it seemed to hide the other characteristic. Gregor Mendel was born as the middle child and only son of Anton and Rosine Mendel. Over the course of his study he observed that there were seven characteristics in the pea plants, and two forms of each characteristic. Gregor Mendel See all media Born: Czech Republic Died: July 20, 1822 January 6, 1884 Brno Czech Republic Subjects Of Study: Mendelian inheritance gene hybridization principle of independent assortment principle of segregation (Show more) Who was Gregor Mendel? He studied a total of seven characteristics. Mendels experiments with pea plants began in 1856. WebHe was elected abbot of his parish in 1868 and became a political activist in his later years, during which time he protested the taxation of his parish. They also have both male and female reproductive parts, so they can either cross-pollinate or self-pollinate. Gregor Mendel was a monk, teacher, and scientist whose research on hybrid pea plants led to the founding principles of modern genetics, as well as to his nickname as the Father of Modern Genetics. thus in the ratios 1: 2: 2: 4: 1: 2: 1: 2: 1, but the distinct Mendel's discovery of these traits in hybrid pea plants was significant for modern genetics, because it enabled Mendel to formulate the laws of independent assortment and segregation. geography of plants, intrinsically connected with statistics. As a child he worked in the garden and studied beekeeping which cultivated in him a deep love for biological sciences. See Bishop, B. E. 1996. His work, however, was still largely unknown. Gregor Mendel (July 20, 1822 - January 6, 1884), known as the Father of Genetics, is most well-known for his work with breeding and cultivating pea plants, using them to gather data about dominant and recessive genes. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. at the Realschule in Brno and continued to carry out some ecclesiastic duties. Where and when did gregor Mendel die? This allowed Mendel to easily study how dominant and recessive traits were inherited in pea plants. In 1848 Mendel became curate but his sensitivity hindered his duties and in 1849 genetics was called an idealistic science contrary to dialectical materialism and How does this demonstrate the ThalattosuchiansExtinct Crocodile Relatives? AAAS, founded in 1848, has evolved into the world's largest multidisciplinary scientific society with nearly 130,000 members and subscribers. In 1851, he transferred to the University of Vienna, where he studied physics and mathematics. Ultimately he died of a kidney disease and cardiac hypertrophy in 1884. https://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Mendel,_Johann_Gregor&oldid=53171. He then joined a monastery in Silesia (now Poland), where he began conducting experiments on plants. He died, aged 61, of kidney disease on January 6, 1884. We all know life when we see itbut what is it REALLY? Based on his work, he produced the paper Experiments on Plant Hybridization and read it to the Natural History Society of Brnn in 1865. Using the ratios for the other six traits in the F1 generation, Mendel was able to identify the other dominant alleles in pea plants, such as round seed shape, yellow seed color, and inflated pod shape. This allows organisms such as the pea plant to randomly receive a combination of alleles for flower color, seed size, and seed shape based upon chance alone. Mendel held liberal views and in 1848 he co-signed a petition for granting civil rights to members of religious orders. Gregor Mendel is often called the father of genetics for his discovery of the basic laws of inheritance. Though Mendel cannot speak for himself today and defend his work, his life as a priest testifies to his faith in the Creator God. In 1857, Mendel began a series of experiments with pea plants that would eventually lead to his discovery of the basic principles of genetics. It wasnt until after his death that other scientists began to realize the significance of his work. However, when crossing pollen from a purple flower with a white flower, Mendel discovered that plants of the F1 generation always possessed purple flowers. A famous composer played the organ at his funeral. This reasoning is an application of Mendel's First Law (of Gregor Mendel, born as Johann Mendel, was an Austrian scientist and monk hailed as the Father of modern genetics for his pioneering research in the field of heredity. Although Mendel continued beyond the P, F1, and F2 generations, the ratios of traits seen in these first three generations represented the foundations for Mendel's discoveries. co-signed a petition for granting civil rights to members of Read on for some interesting facts about Gregor Mendels death. crises caused by strained circumstances and an uncertain future, he completed In those days, Metabolism is the totality of chemical reactions that manage all of the molecular, material, and energy resources within an organism. in equal proportions. and offspring with regard to some trait rather than studying the theory of WebGregor Johann Mendel (Heinzendorf, Austria, 20 July 1822 Brnn, Austro-Hungary, 6 January 1884) was an Austrian monk and botanist. After acquainting himself with Darwin's After his death, the succeeding abbot burned all papers in Mendel's collection, to mark an end to the disputes over taxation. In 1843, after mental Gregor Mendel died on January 6th, 1884 in Brno, Moravia. In 1850, nervous and lacking university education, he failed one of the Nitrogen Fixation in Plants & Humans | What is Nitrogen Fixation? In 1860, Mendel was appointed Professor of Natural History and Director of the Botanical Garden at the Moravian capital of Brno. Meiosis Steps & Results | What is Meiosis? The study showed that out of four plants, one received recessive alleles, two were hybrids, and one had the dominant alleles. It was there that Mendel began his famous plant-breeding experiments. could well have been at the back of his mind. Being a monk, he never married and led a life of celibacy. The European Mathematical Society. Mendel spent several years conducting research at both institutions before returning to his hometown to become a monk. By studying the ratios of traits found in each generation, Mendel discovered that alleles, or alternate forms of a gene, were responsible for the phenotypes, or traits observed in living organisms. I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. Although he published his work in 1866, his research did not receive recognition until the 1900s. In 1865, Mendel presented his findings to the Natural History Society of Brno but they were largely ignored. Man of Science, Man of God: Gregor Johann Mendel. (2020, August 28). how did gregor mendel die. Create your account. In 1856, Mendel was sent to study at the University of Vienna. Kelly has taught High School Science and Applied Communications. In 1843, he entered an Augustinian monastery in Brno (now in the Czech Republic) and took the name Gregor. Fisher (1936) He is famous for his work on heredity, which has led to many discoveries in genetics today. Of course, his system eventually proved to be of general application and is one of the foundational principles of biology. The cause of death is unknown but it is speculated that he may have had liver or kidney problems. 34 of their varieties for the constancy of traits, and selecting 22 of them. and even Maupertuis (see Glass, 1959). Mendel began his famous experiments with pea plants in 1856. His methods of conducting research also led to the formulation of the laws of independent assortment and segregation. Mendel's paper was rejected at first, since he evidently produced it as a counter to Darwin's theory of pangenesis, which was popular at the time and accepted as being responsible for inheritance.2 In 1868, Mendel was elevated to the position of abbot, and his scientific work was largely displaced by his administrative and ministerial responsibilities. Known For: Scientist, friar, and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey who gained posthumous recognition as the founder of the modern science of genetics. And indirect evidence including his meteorological work indicates that Mendel He published his results in 1865, but they were largely ignored at the time. concluded that Mendel had correctly described their layout, but that their Reference: gregor mendel experiments. His experiments were the foundation for two generalizations known today as Mendel's Laws of Inheritance. Mendel was born in 1822 in Heinzendorf, Austria (now Hyn\u{c}ice, Czech Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support. Austrian Meteorological Society. Leadership. Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams son, oliver tony adams son, oliver After creating a true-breeding parent generation, Mendel created hybrid plants for the F1 generation, which were then allowed to self-pollinate in order to produce the plants of the F2 generation. The society published the paper in its Proceedings in 1866. Mendel died in 1884, before he could see the full impact of his work. Mendel, Darwin and Fisher. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. He cross-pollinated the plants with contrasting characteristics in order to study the effects on the offspring. succeed. My scientific studies have afforded me great gratification; and I am convinced that it will not be long before the whole world acknowledges the results of my work. Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the "Father of Modern Genetics". During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate, with one chromosome from each parent randomly assigned to each new gamete. He was one of the first to apply statistical It was during this time that he began to conduct his famous experiments on plant hybridization. Gregor Mendel died on January 6th, 1884 in Brno, Moravia. But the number six appears to overshadow natures mathematical landscape. Mendel indeed studied mathematics and the natural sciences there Mendels work laid the foundations for the modern science of genetics. He became an Augustinian monk in 1843 and later studied at the University of Vienna. how did gregor mendel die. He was a monk in Augustinian Abbey of St Thomas in Brno where he worked as a teacher. as well as alleles and gametes, being later Experiments in plant hybridization. Education: University of Olomouc, University of Vienna. www.springer.com As a child, he worked alongside his father to improve the family orchards by grafting, a practice encouraged and sponsored by the land's feudal proprietor, the Countess Maria Truchsess-Ziel.1 Since grafting was a particular "art" that produced both desirable and undesirable results, working in the orchards introduced the young Mendel to the beginnings of his experimental botany work. Mendel was the son of a small-scale farmer and had seven brothers and sisters. In other words, the offspring will always be the same as their parents. The mission, to "advance science, engineering, and innovation throughout the world for the benefit of all people," has propelled the organization to the forefront of national and international initiatives. Polygenic Inheritance Example, Genes & Disease | What is Polygenic Inheritance? Why is Gregor Mendel famous? He cultivated thousands of pea plants over the course of his experiments. Mendel founded genetics by his work cross-breeding pea plants. She has taught a combination of ESL and STEM courses to secondary and university students. Czech composer Leo Janek played the organ at his funeral. Science and policy programs include the major annual forum on Science & Technology policy, S&T policy fellowships within the US Congress and government agencies, and the tracking of US funding for R&D research. At that time, the monastery was a cultural center for the region, and Mendel was immediately exposed to the research and teaching of its members, and also gained access to the monasterys extensive library and experimental facilities. But his research failed to create an impact at that time. The cause of his death is not certain, but it is generally believed to be due to either stroke or kidney failure. Gregor Mendel See all media Born: Czech Republic Died: July 20, 1822 January 6, 1884 Brno Czech Republic Subjects Of Study: Mendelian inheritance gene hybridization principle of independent assortment principle of segregation (Show more) Who was Gregor Mendel? In 1868, Mendel was appointed abbot of his monastery. genotypic structure according to $(AB + aB + Ab + ab)^2$. Gregor Mendel See all media Born: Czech Republic Died: July 20, 1822 January 6, 1884 Brno Czech Republic Subjects Of Study: Mendelian inheritance gene hybridization principle of independent assortment principle of segregation (Show more) Who was Gregor Mendel? Yet so important was this Best Known For: Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who discovered the basic principles of heredity through experiments in his garden. His paper was published the following year, but it was not widely read or understood at the time. During his lfe, Mendel participated in local agricultural affairs. Although other scientists of the period conducted similar experiments into the inheritance of traits, they were unsuccessful in proving or disproving how traits were passed down from one generation to the next. Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the "Father of Modern Genetics". In 1868, Mendel was elected abbot of the school where he had been teaching for the previous 14 years, and both his resulting administrative duties and his gradually failing eyesight kept him from continuing any extensive scientific work. with $b$ recessive. sequential procedure, so that Fisher's opinion was only partly correct and In 1843, he began his training as a priest and joined the Augustinian Abbey of St Thomas in Brno as a monk. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Gregor-Mendel, https://www.biography.com/scientist/gregor-mendel, https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/gregor-mendel-a-private-scientist-6618227/, Copyright 2023 bindscience.com | Powered by Digimetriq. Gregor Mendel died on January 6, 1884, at the age of 61. of tornadoes in 1871, although it went unnoticed at the time. WebGregor Mendel, (born July 22, 1822, Heinzendorf, Austriadied Jan. 6, 1884, Brnn, Austria-Hungary), Austrian botanist and plant experimenter who laid the mathematical foundation of the science of genetics. Who: Gregor Johann Mendel
In 1854 he was appointed teacher of physics, zoology and botany He was sent to the University of Vienna between 1851 and 1853 to study botany, zoology, chemistry, and physics, and returned to the abbey in Brnn to teach. Gregor Mendel, a 19th-century Austrian monk, discovered the law of segregation. There he studied physics and mathematics under Christian Doppler and botany from Franz Unger. He cross-fertilized pea plants that had clearly opposite characteristicstall with short, smooth with wrinkled, those containing green seeds with those containing yellow seeds, etc.and, after analyzing his results, reached two of his most important conclusions: the Law of Segregation, which established that there are dominant and recessive traits passed on randomly from parents to offspring (and provided an alternative to blending inheritance, the dominant theory of the time), and the Law of Independent Assortment, which established that traits were passed on independently of other traits from parent to offspring.
independent assortment of alleles). to Vienna. van der Waerden, B.L. On certain aspects of the evolutionary process from the standpoint of modern genetics. He had two sisters and the family lived and worked on the farm they had owned for generations. For terms and use, please refer to our Terms and Conditions He spent about seven years planting, breeding and cultivating pea plants in an experimental part of the abbey garden that was started by the previous abbot. Even then, however, his work was often marginalized by Darwinians, who claimed that his findings were irrelevant to a theory of evolution. As a federally recognized 501(c)(3) nonprofit ministry of the USA, all gifts to ICR are completely tax deductible to the fullest extent allowed by U.S. law. Scoville, Heather. He aimed at achieving practical results, but a simultaneous study of heredity These were called monohybrid experiments. WebDied: January 6, 1884 Claim to fame: discovered the basic laws of genetics through experiments with pea plants Known for: breeding thousands of pea plants and observing how parent plants' characteristics are passed on from generation to generation Significance: Mendel's experiments started the science of genetics Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams. Whether Mendel, G., A. Corcos, and F. Monaghan. This Is the Crew of the Artemis II Mission, Your Privacy Choices: Opt Out of Sale/Targeted Ads, Name: Gregor Mendel, Birth Year: 1822, Birth date: July 20, 1822, Birth City: Heinzendorf, Birth Country: Austria. WebDied: January 6, 1884 Claim to fame: discovered the basic laws of genetics through experiments with pea plants Known for: breeding thousands of pea plants and observing how parent plants' characteristics are passed on from generation to generation Significance: Mendel's experiments started the science of genetics
 Ultimately he died of a kidney disease and cardiac hypertrophy in 1884. The Significance of Gregor Mendels Work Gregor Mendel is [21] The Famous Celebrity Your Source for All Things Celebrity From 1875 he objected to the unjust (in his opinion) taxation of his monastery. In fact, it was not until after Mendels death that his work began to receive any significant attention. Furthermore, Mendel's findings were not viewed as being generally applicable, even by Mendel himself, who surmised that they only applied to certain species or types of traits. of quantitative traits was a corollary of the Mendelian laws (Kolmogorov, In Bateson, W. de Beer, G. (1964, 1966). Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the "Father of Modern Genetics". Astrological Sign: Cancer, Death Year: 1884, Death date: January 6, 1884, Death City: Brno, Death Country: Austria, Article Title: Gregor Mendel Biography, Author: Biography.com Editors, Website Name: The Biography.com website, Url: https://www.biography.com/scientists/gregor-mendel, Publisher: A&E; Television Networks, Last Updated: May 21, 2021, Original Published Date: April 2, 2014. correctly explained the origin WebHe died in 1884, aged 62. Republic) into a peasant family of German--Czech origin.
Ultimately he died of a kidney disease and cardiac hypertrophy in 1884. The Significance of Gregor Mendels Work Gregor Mendel is [21] The Famous Celebrity Your Source for All Things Celebrity From 1875 he objected to the unjust (in his opinion) taxation of his monastery. In fact, it was not until after Mendels death that his work began to receive any significant attention. Furthermore, Mendel's findings were not viewed as being generally applicable, even by Mendel himself, who surmised that they only applied to certain species or types of traits. of quantitative traits was a corollary of the Mendelian laws (Kolmogorov, In Bateson, W. de Beer, G. (1964, 1966). Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk, teacher, and scientist who is commonly referred to as the "Father of Modern Genetics". Astrological Sign: Cancer, Death Year: 1884, Death date: January 6, 1884, Death City: Brno, Death Country: Austria, Article Title: Gregor Mendel Biography, Author: Biography.com Editors, Website Name: The Biography.com website, Url: https://www.biography.com/scientists/gregor-mendel, Publisher: A&E; Television Networks, Last Updated: May 21, 2021, Original Published Date: April 2, 2014. correctly explained the origin WebHe died in 1884, aged 62. Republic) into a peasant family of German--Czech origin.